Buy ATEX Hoist
Atex hoists provide explosion protection. Consequently they are designed to prevent a potential source of ignition to any incidence of explosive mixtures. As a result ATEX rated equipment is used in a wide range of industries where these types of hazards occur.
£451.50 – £1,685.10
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
What is an Atex hoist?
Firstly the word ATEX is derived from ATmosphere EXplosibles. ATEX is used to describe any equipment which can be used in environments with potentially explosive atmospheres. For example an ATEX rated lever hoist.Where are ATEX Hoists used?
Examples of industries which may use an atex hoist include: chemical plants, waste disposal, energy production, gas suppliers, metal processing. Others areas include paint shops, pharmaceuticals, oil refineries and many more. Furthermore they all use combustible materials and will all need to lift materials/goods at some point. Therefore Atex equipment is essential.What ATEX Hoists are Available?
 Lifting Hoists Direct can supply a range of atex hoist systems with ratings suitable for these scenarios. Firstly we have ATEX chain blocks / manual chain hoists and Lever hoists. Secondly we have Air hoists. They all come in a range of lifting capacities and zone classifications. In addition all our atex hoist devices come complete with full Atex certification.
Lifting Hoists Direct can supply a range of atex hoist systems with ratings suitable for these scenarios. Firstly we have ATEX chain blocks / manual chain hoists and Lever hoists. Secondly we have Air hoists. They all come in a range of lifting capacities and zone classifications. In addition all our atex hoist devices come complete with full Atex certification.
What does ATEX rated mean?
Here we have provided some very basic information regarding ATEX rated equipment and explosion proof hoists. Consequently the environments they are used in will also be addressed for your convenience. Primarily because an atex hoist rating can vary. Above all it is your responsibility to carry out necessary research to ensure all safety aspects are correctly covered.What are Explosive Environments?
Flammable gasses, mists, vapours and combustible dusts can all cause explosive atmospheres. Therefore suitable measures must be taken. There are 3 factors required to cause an explosion A = Flammable substance i.e. gas, dust, mist, vapour B= Oxidizing agent i.e. oxygen (in the air) C= Ignition Source i.e. Spark, flame, hot surface, static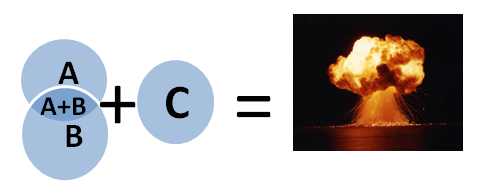
What Does Explosion Protection Mean?
An explosion proof hoist has special explosion protection, thus preventing explosions occurring. This is because of the removal of potential sources of ignition. Consequently specialised components are used together with ongoing monitoring of potentially hazardous situations. There are three types of explosion protection within atex regulations, therefore it is most important to get the correct equipment. PRIMARY PROTECTION = Preventing the formation of explosive atmospheres SECONDARY PROTECTION = Preventing the ignition of potential explosive atmospheres TERTIARY PROTECTION = Restricting the effects of an explosion.Atex Zones Explained
There are six atex rating zone classifications in which an Atex hoist may be used. However they cover the different types of explosive environments. Therefore you will find three for gas and vapour hazards and three for dust hazards. But Atex zone 1 and Atex zone 2 are the most common. An explosion proof hoist will fit into one of these categories. So here are the atex zones explained in a little more detail . In order to help you choose the correct atex hoist and most importantly, comply with atex regulations. 1, Atex Zone 0 (Gas/Vapours) Areas where explosive mixtures are always present or present for long periods. 2, Atex Zone 1 (Gas/Vapours) Areas where explosive mixtures are likely to occur in normal operating conditions. 3, Atex Zone 2 (Gas/Vapours) Areas where explosive mixtures are not likely to occur in normal operation & is it does occur only for a short time. 4, Atex ZONE 20 (Dust) Areas where explosive mixtures are always present or there for long periods. 5, Atex ZONE 21 (Dust) Areas where explosive mixtures are likely to occur in normal operating conditions. 6, Atex ZONE 22 (Dust) Areas where explosive mixtures are unlikely to occur in normal operating conditions and if it does, only for a short time.Equipment Groups, Zone Classification, Protection Levels & Categories
| GROUP | CATEGORY | PROTECTION LEVEL | RISK ZONE |
| l Mining | M (1) | Mechanical Equipment – Energised VERY HIGH protection – equipment must continue to operate in explosive atmosphere | 0, 1, 2 (gasses) 20, 21, 22 (dust) |
| ll Mining | M (2) | Mechanical Equipment – De-energised HIGH protection. Equipment must be shut down if explosive atmosphere occurs | 1, 2 (gasses) 21, 22 (dust) |
| ll Non-Mining | 1 | VERY HIGH protection, where dust, gas or vapour mixtures are present continuously or for long periods | 0, 1, 2 (gasses) 20, 21, 22 (dust) |
| ll Non-Mining | 2 | HIGH level protection where dust, gas or vapour mixtures are likely to occur occasionally | 1, 2 (gasses) 21, 22 (dust) |
| ll Non-Mining | 3 | NORMAL protection where gasses, dust or vapour mixtures are NOT likely to occur & if they do only for a short time. | 2 (gasses) 22 (dust) |
Temperatures
Temperatures can have a major effect within explosive environments, therefore extreme caution should be implemented. The table below shows the temperature at which a gaseous mixture will ignite spontaneously without a further ignition source. Consequently you should always be aware of temperatures in your work environment.| TEMPERATURE CLASSES | MAXIMUM SURFACE TEMPERATURE | IGNITION TEMPERATURE RANGE OF MIXTURES |
| T1 | 450◦C | >450◦C |
| T2 | 300◦C | >300 - 450◦C |
| T3 | 200◦C | >200 - 300◦C |
| T4 | 135◦C | >135 - 200◦C |
| T5 | 100◦C | >100 - 135◦C |
| T6 | 85◦C | >85 - 100◦C |
Atex Rated Markings Decrypted
All ATEX rated equipment should be clearly marked to ensure it is easily identifiable. Most importantly to which group, category, zone and protection type it is suitable for. This guide shows you how to interpret the marks. Atex certification should always be issued, retained and referred to with these types of hoisting devices.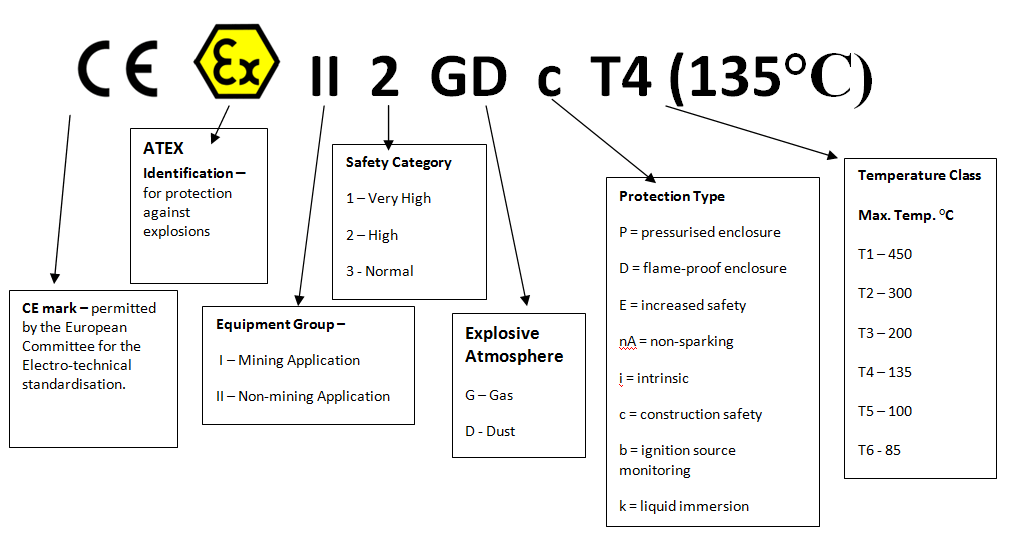 We hope you have found this Atex hoist page informative, but please contact us if you need more information.
We hope you have found this Atex hoist page informative, but please contact us if you need more information.
 Fast Delivery
Fast Delivery Low Prices
Low Prices Buy Online
Buy Online





